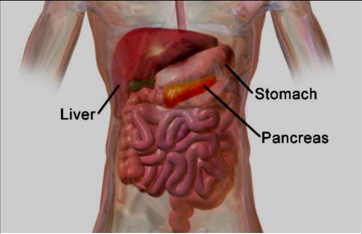
Pancreatic cancer is cancer that forms in the cells of the pancreas. The pancreas is the pear-shaped organ located behind your stomach. The function of the pancreas is to:
- Produce enzymes that help digest your food
- Make hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which help control your blood sugar levels
Types of Pancreatic Cancer
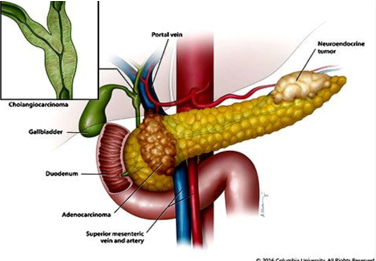
There are two types of pancreatic cancer. The most common type develops in the cells that make digestive enzymes. This is called pancreatic exocrine cancer and makes up more than 95% of all cancers of the pancreas.
The other type of cancer develops in the cells responsible for making hormones, including the ones that help manage blood sugar. This type is called pancreatic endocrine cancer and makes up less than 5% of all pancreatic cancers.
Causes of Pancreatic Cancer
The exact causes of pancreatic cancer are not known. However, there are some environmental and genetic factors that may increase your chances of developing cancer. These include:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Chronic inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis)
- Liver damage
- Family history of pancreatic cancer
- Sixty-five years of age or older
- Family history of pancreatic cancer
- Family history of certain genetic disorders that have been linked to this type of cancer (e.g. Lynch syndrome)
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of pancreatic cancer often do not occur until the disease is advanced. These may include:
- Pain in the back or belly
- Light-coloured and/or greasy stools
- Dark-coloured urine
- Yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice)
- Loss of appetite or unintended weight loss
- Itchy skin
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- New diagnosis of diabetes or existing diabetes that’s becoming more difficult to control
See your doctor if you experience any unexplained symptoms that worry you. Many other conditions can cause these symptoms, so your doctor may check for these conditions as well as for pancreatic cancer.
Diagnosis
You will need to have a number of tests and scans to check for pancreatic cancer if a doctor refers you to a specialist.
These tests can include:
- Blood tests
- Scans, like an ultrasound (sometimes from inside your body using an endoscope), CT scan, PET scan, or MRI scan
- Biopsy: the removal of a small sample of cells from the pancreas (to be checked for cancer)
- Laparoscopy which is a small operation to look inside your tummy
Prevention Tips
Although you can inherit genes that increase your risk for pancreatic cancer, you can make lifestyle changes to help reduce your risk. You can:
- Choose a healthy diet. A diet full of colorful fruits and vegetables and whole grains may help reduce your risk of cancer.
- Maintain or aim for a healthy weight. Being overweight or obese is a leading risk factor for several types of cancer.
- Stop smoking if you smoke. Smoking increases your risk for several types of cancer, including pancreatic cancer.
- Avoid or reduce alcohol intake. Heavy drinking may increase your risk for chronic pancreatitis and possibly pancreatic cancer.
.
.
Test you knowledge on Pancreatic Cancer by clicking the link below.
https://forms.gle/Mxf5mSvW4aX4EGxm8
.
.
Information sources:
Mayo Clinic Johns Hopkins Medicine
Produced by:
The Health Promotion Department
Ministry of Health & Social Security
Botanical Gardens, Tanteen, St. George’s
Tel: (473) 440-2649/3485
hpgrenada@hotmail.com
www.facebook.com/HealthGrenada
http://www.gov.gd/moh/

